InternBook Developer Guide
Acknowledgements
- https://nus-cs2103-ay2324s2.github.io/website/
- https://se-education.org/guides/conventions/markdown.html
- https://se-education.org/guides/conventions/java/intermediate.html
- https://se-education.org/guides/conventions/git.html
Setting up, getting started
Refer to the guide Setting up and getting started.
Design
Architecture
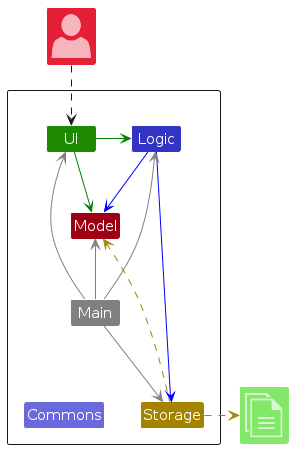
The Architecture Diagram given above explains the high-level design of the App.
Given below is a quick overview of main components and how they interact with each other.
Main components of the architecture
Main (consisting of classes Main and MainApp) is in charge of the app launch and shut down.
- At app launch, it initializes the other components in the correct sequence, and connects them up with each other.
- At shut down, it shuts down the other components and invokes cleanup methods where necessary.
The bulk of the app's work is done by the following four components:
UI: The UI of the App.Logic: The command executor.Model: Holds the data of the App in memory.Storage: Reads data from, and writes data to, the hard disk.
Commons represents a collection of classes used by multiple other components.
How the architecture components interact with each other
The Sequence Diagram below shows how the components interact with each other for the scenario where the user issues the command delete 1.

Each of the four main components (also shown in the diagram above),
- defines its API in an
interfacewith the same name as the Component. - implements its functionality using a concrete
{Component Name}Managerclass (which follows the corresponding APIinterfacementioned in the previous point.
For example, the Logic component defines its API in the Logic.java interface and implements its functionality using the LogicManager.java class which follows the Logic interface. Other components interact with a given component through its interface rather than the concrete class (reason: to prevent outside component's being coupled to the implementation of a component), as illustrated in the (partial) class diagram below.

The sections below give more details of each component.
UI component
The API of this component is specified in Ui.java
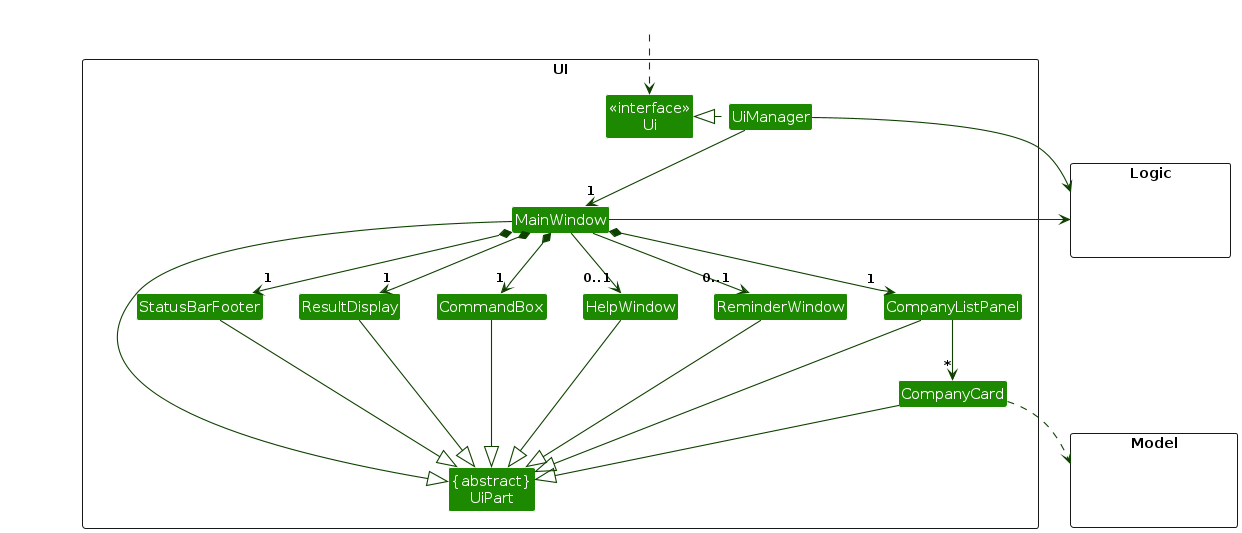
The UI consists of a MainWindow that is made up of parts e.g.CommandBox, ResultDisplay, CompanyListPanel, StatusBarFooter etc. All these, including the MainWindow, inherit from the abstract UiPart class which captures the commonalities between classes that represent parts of the visible GUI.
The UI component uses the JavaFx UI framework. The layout of these UI parts are defined in matching .fxml files that are in the src/main/resources/view folder. For example, the layout of the MainWindow is specified in MainWindow.fxml
The UI component,
- executes user commands using the
Logiccomponent. - listens for changes to
Modeldata so that the UI can be updated with the modified data. - keeps a reference to the
Logiccomponent, because theUIrelies on theLogicto execute commands. - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent, as it displaysCompanyobject residing in theModel.
Logic component
API : Logic.java
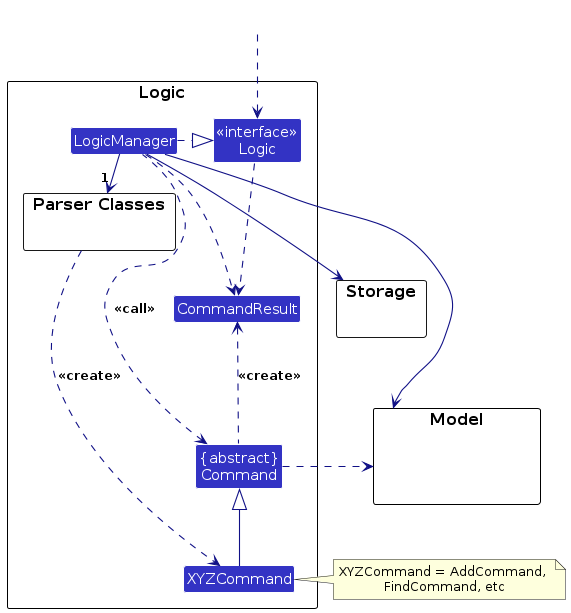
Here's a (partial) class diagram of the Logic component:
The sequence diagram below illustrates the interactions within the Logic component, taking execute("delete 1") API call as an example.
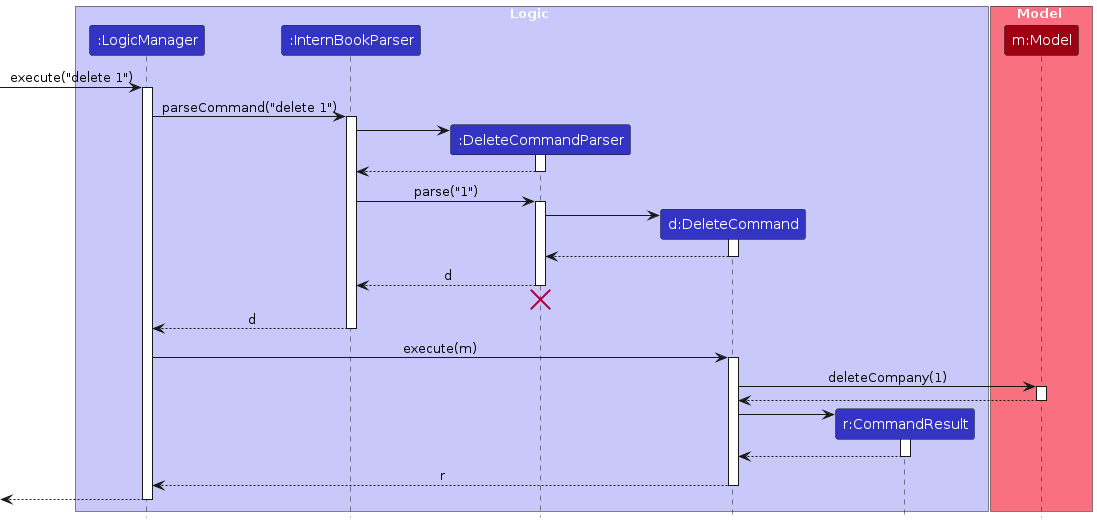
Note: The lifeline for DeleteCommandParser should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline continues till the end of diagram.
How the Logic component works:
- When
Logicis called upon to execute a command, it is passed to anInternBookParserobject which in turn creates a parser that matches the command (e.g.,DeleteCommandParser) and uses it to parse the command. - This results in a
Commandobject (more precisely, an object of one of its subclasses e.g.,DeleteCommand) which is executed by theLogicManager. - The command can communicate with the
Modelwhen it is executed (e.g. to delete a company).
Note that although this is shown as a single step in the diagram above (for simplicity), in the code it can take several interactions (between the command object and theModel) to achieve. - The result of the command execution is encapsulated as a
CommandResultobject which is returned back fromLogic.
Here are the other classes in Logic (omitted from the class diagram above) that are used for parsing a user command:

How the parsing works:
- When called upon to parse a user command, the
InternBookParserclass creates anXYZCommandParser(XYZis a placeholder for the specific command name e.g.,AddCommandParser) which uses the other classes shown above to parse the user command and create aXYZCommandobject (e.g.,AddCommand) which theInternBookParserreturns back as aCommandobject. - All
XYZCommandParserclasses (e.g.,AddCommandParser,DeleteCommandParser, ...) inherit from theParserinterface so that they can be treated similarly where possible e.g, during testing.
Model component
API : Model.java
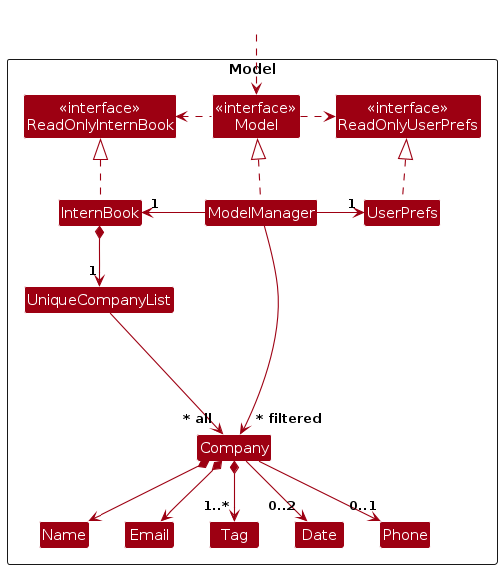
The Model component,
- stores the address book data i.e., all
Companyobjects (which are contained in aUniqueCompanyListobject). - stores the currently 'selected'
Companyobjects (e.g., results of a search query) as a separate filtered list which is exposed to outsiders as an unmodifiableObservableList<Company>that can be 'observed' e.g. the UI can be bound to this list so that the UI automatically updates when the data in the list change. - stores a
UserPrefobject that represents the user’s preferences. This is exposed to the outside as aReadOnlyUserPrefobjects. - does not depend on any of the other three components (as the
Modelrepresents data entities of the domain, they should make sense on their own without depending on other components)
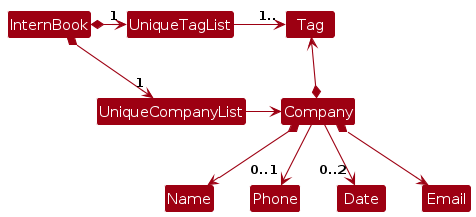
Note: An alternative (arguably, a more OOP) model is given below. It has a Tag list in the InternBook, which Company references. This allows InternBook to only require one Tag object per unique tag, instead of each Company needing their own Tag objects.
Storage component
API : Storage.java
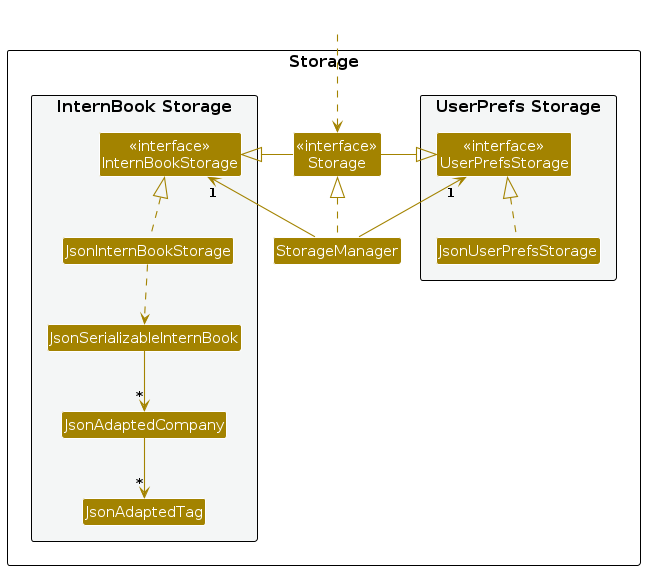
The Storage component,
- can save both address book data and user preference data in JSON format, and read them back into corresponding objects.
- inherits from both
InternBookStorageandUserPrefStorage, which means it can be treated as either one (if only the functionality of only one is needed). - depends on some classes in the
Modelcomponent (because theStoragecomponent's job is to save/retrieve objects that belong to theModel)
Common classes
Classes used by multiple components are in the seedu.addressbook.commons package.
Implementation
This section describes some noteworthy details on how certain features are implemented.
Setting Reminder
Implementation
The reminder feature is supported by the Reminder class, which is associated with the Days and ReminderOnOff class.
Reminder class keeps track of two values which are days and reminderOnOff.
days- ADaystype that keeps track of the number of days, the user input, from the end date of an application.reminderOnOff- AReminderOnOfftype that keeps track whether the reminder feature is on or off.
Reminder implements the following relevant methods:
Reminder(Days days, ReminderOnOff reminderOnOff)- Constructor for reminder with days and reminderOnOff specified.getDays()- Gets the number of days before the deadline to trigger the reminder.getReminderOnOff- Gets the status of the reminder.
An example usage scenario for setting reminder is as follows:
Step 1: The user launches the application and the Ui loads up.
Step 2: The user inputs a command to set reminder using the reminder command.
Step 3: The LogicManager takes the user input and parses it using SetReminderParser, which in turn creates a SetReminderCommand.
object.
Step 4: SetReminderCommand#execute is called, which keeps track of the reminder passed into the constructor.
Step 5: The Model saves the user's input into a json file.
The sequence diagram below shows how the reminder command works within the Logic component.
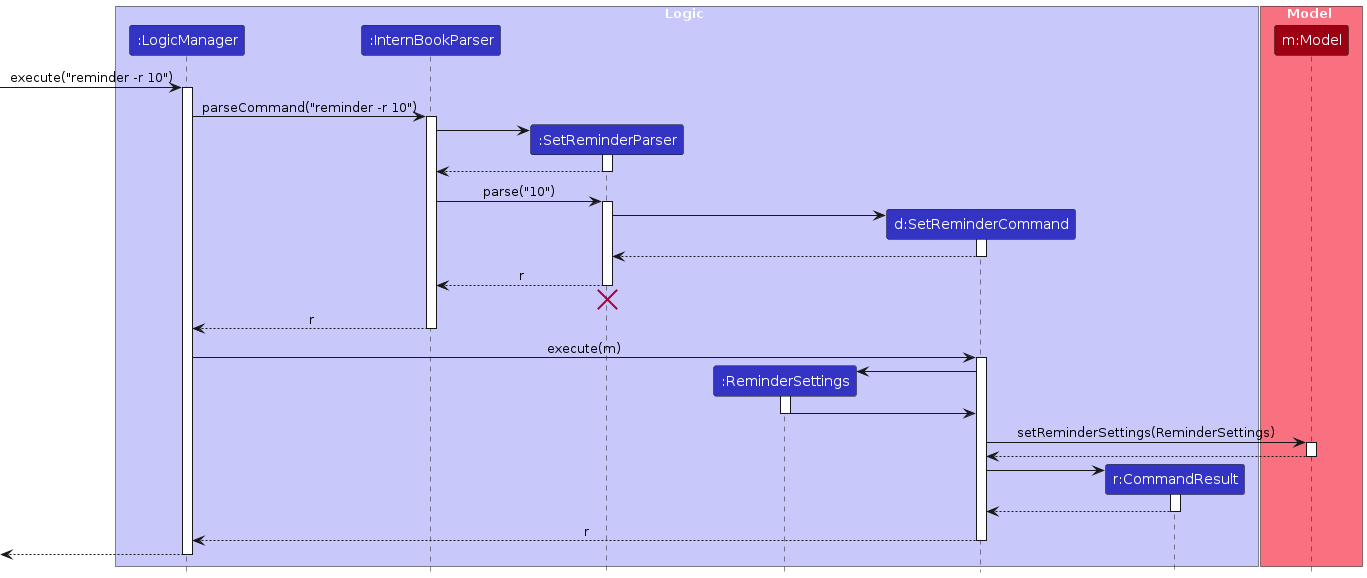
The activity diagram below summarizes the process of setting a reminder:
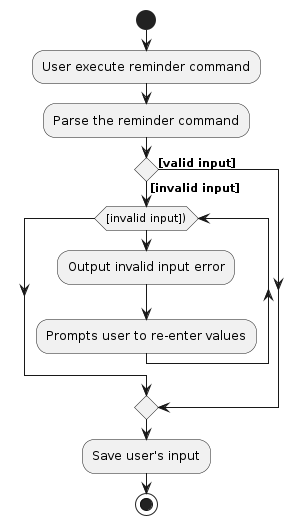
Design considerations:
Error Handling
- Ensure robust error handling to gracefully manage exceptions and failures during command execution.
- Utilise the
CommandExceptionclass to handle and propagate errors consistently.
Input Validation:
- Validate user input to ensure it meets the expected format and constraints.
- Verify that the number of days provided is a valid integer and within an acceptable range.
Separation of Concerns
- Separate the parsing of user input from the execution logic to improve code.
- Consider creating a dedicated parser class responsible for converting user input into a
Reminderobject.
Storing of User's Input
- Storing user's preference for reminder feature into a json file.
- Preference is saved for future usage.
Find feature
Implementation
The find mechanism is facilitated in two parts, the first by the FindCommandParser, and then the FindCommand
Given below is a step-by-step detailed guide on how the find mechanism works.
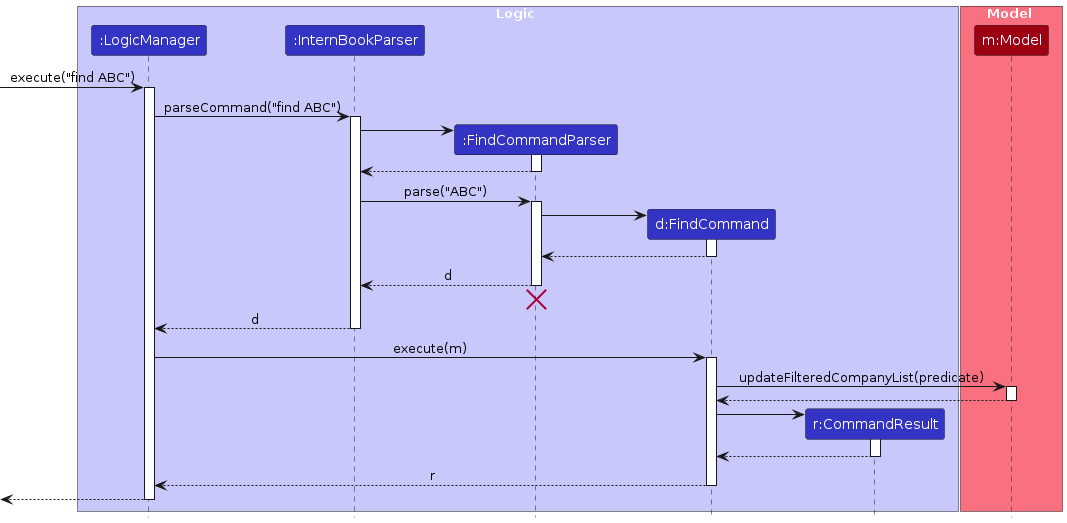
Step 1. The user launches the application. This does not affect anything in the find command pathway.
Step 2. The user executes find ABC command in order to find all entries matching the name or tag ABC.
Step 3. The FindCommandParser parses the information directly to identify the keyword to be found.
Displayed in the diagram below is how the FindCommandParser interacts while parsing the information.
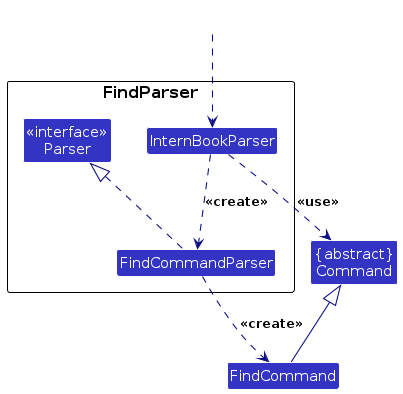
Step 4. A NameContainsKeywordPredicate object is created, which inherits Predicate<Company> and overrides a Test method which determines whether a certain company is a match.
Step 5. A FindCommand instance is created, initializing the NameContainsKeywordPredicate as relevant.
Step 6. The FindCommand goes through its execution cycle, facilitated by Model
Step 7. The Model filters the Company List based on the predicate, and returns the filtered list.
The sequence diagram below traces the pathway of the find command within the Logic component, taking find ABC API call as an example.
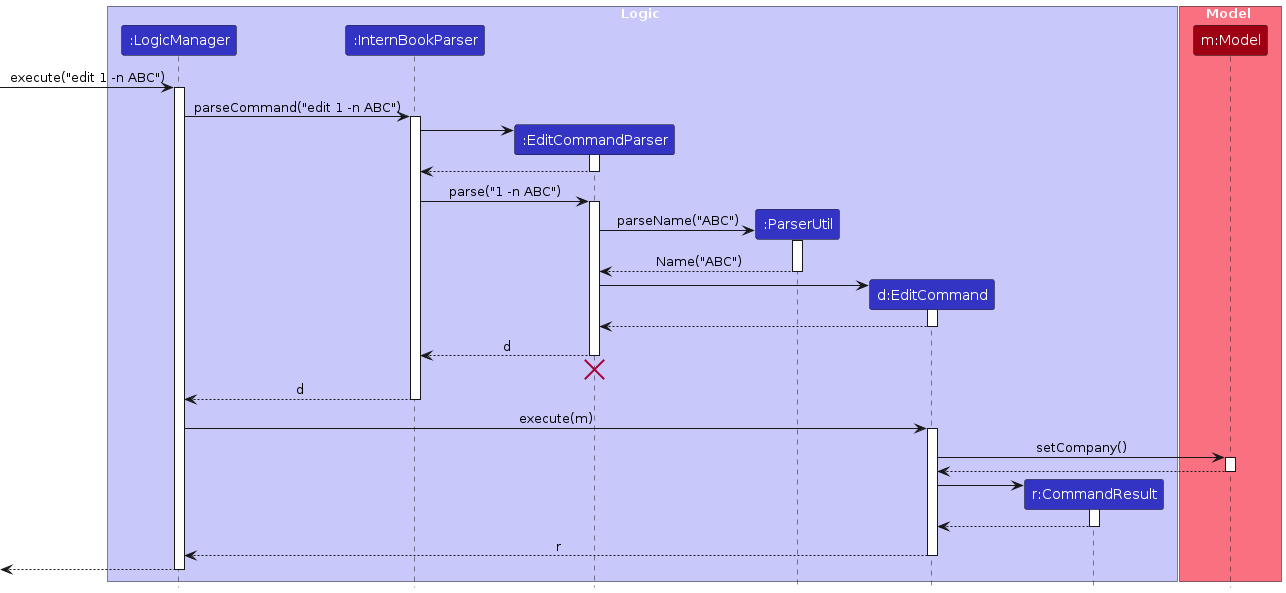
Edit feature
Implementation
The edit mechanism is facilitated in two parts, the first by the EditCommandParser, and then the EditCommand
Given below is a step-by-step detailed guide on how the edit mechanism works.
Step 1. The user launches the application. This does not affect anything in the edit command pathway.
Step 2. The user executes edit 1 -n ABC command in order to edit the name in the first index.
Step 3. The EditCommandParser parses the information through ParserUtil in the command to identify each component.
Displayed in the diagram below is how the EditCommandParser interacts while parsing the information.
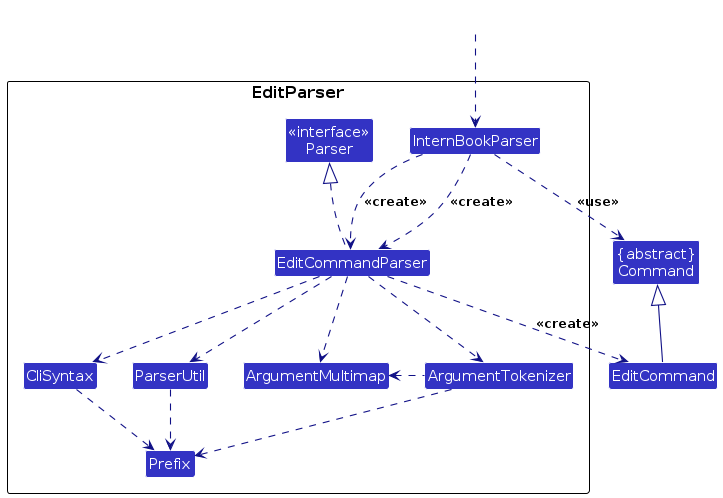
Step 4. This information is encapsulated inside an editCompanyDescriptor, which contains all the values associated with the changed prefixes. In this case, it will set the name of the descriptor to ABC.
Step 5. An EditCommand instance is created, initializing the index and editCompanyDescriptor as relevant.
Step 6. The EditCommand goes through its execution cycle, facilitated by Model
Step 7. The Model retrieves the Company List, and sets the edited company described in the editCompanyDescriptor to the company at index index.
The sequence diagram below traces the pathway of the edit command within the Logic component, taking edit 1 -n ABC API call as an example.
Application date property
Implementation
The date property enables users to keep track of application start and end dates. End dates must be the same or later than start dates.
The implementation of this property is similar to the other properties present in the company entity. The difference lies in the link between start and end dates.
Below are some of the design choices made, as well as alternative implementations possible.
Design choices
- Start and end dates are represented with the same type.
The company entity contains 2 date entities for start and end dates.
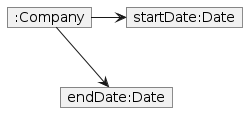 The following alternative implementations explored:
* Have a date range class that represents both the start and end date
* Pros: Easier checking of constraints that apply on both the start and end date
* Cons: Low extensibility. Potentially high coupling between company and date property.
The following alternative implementations explored:
* Have a date range class that represents both the start and end date
* Pros: Easier checking of constraints that apply on both the start and end date
* Cons: Low extensibility. Potentially high coupling between company and date property.
- [!IMPORTANT] Checks on constraints that apply to both start and end dates are handled outside the company class, at the point of Date object creation.
Since the company constructor does not currently throw any exceptions, it would require a huge refactor to enable constraint checks within the constructor.
Hence, the responsibility lies on the caller to check that the start and end dates provided to the company are correct.
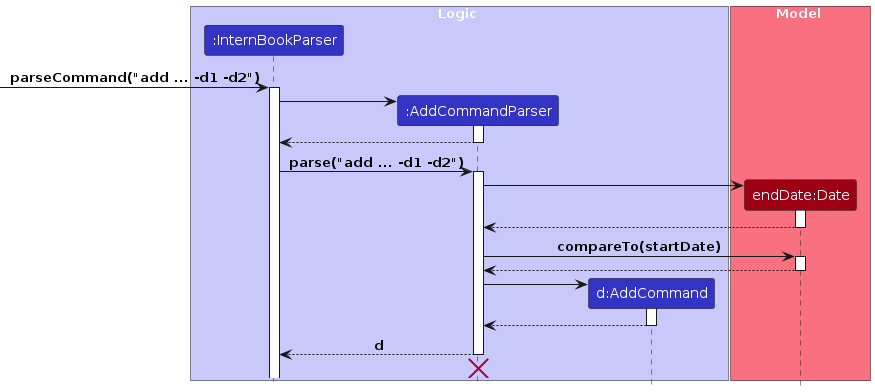
The above diagram shows that the checks are called by the AddCommandParser object.
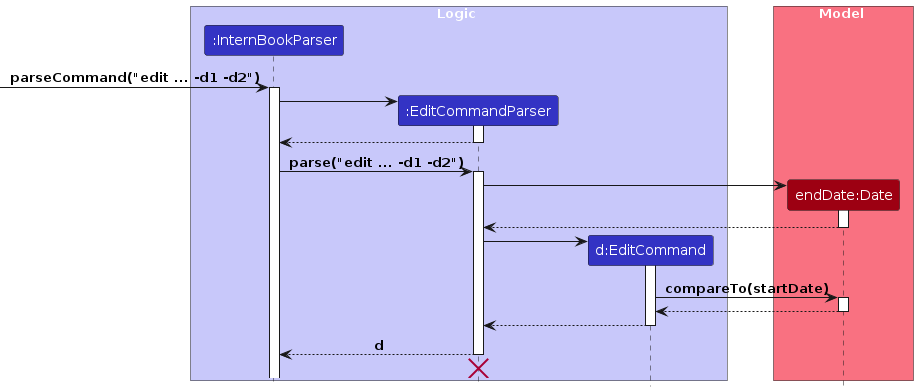
The above diagram shows that the checks are called by the EditCommand instead of the EditCommandParser.
This is admittedly a design flaw that will cause issues when new commands are added. As such, in future implementations, the checks should be done within the company class to ensure that companies cannot be created with dates that violate the constraints.
Sort Feature
Implementation
The sort feature is facilitated by Model and SortType enum. The SortCommand is responsible for sorting the list of companies in the application based on the user's preference. The command supports three sorting types: alphabetical order, start date order, and end date order.
The SortType Enum has 3 values:
ALPHABETICAL_ASCENDING: Sorts the companies alphanumerically.STARTDATE_ASCENDING: Sorts the companies by their starting date.ENDDATE_ASCENDING: Sorts the companies by their ending date.
Sort implements the following relevant operations:
model.sortCompanyListByName()- SortsUniqueCompanyListinInternBookin ascending alphanumerical order.model.sortCompanyListByStartDate()- SortsUniqueCompanyListinInternBookin order of ascending start date.model.sortCompanyListByEndDate()- SortsUniqueCompanyListinInternBookin order of ascending end date.
Given below is a step-by-step detailed guide on how the sort mechanism behaves.
Step 1. The user launches the application.
Step 2. The user inputs a command to sort the companies in the intern book in a specified order using the sort command.
Step 3. The SortCommandParser is responsible for processing user input. It takes the user's input and parses it into one of the three different SortType options available.
Step 4: A SortCommand object will then be called with the chosen SortType as the argument.
Step 5: SortCommand#execute is called, which calls the corresponding model.sortCompanyList
Step 6: The GUI will display the newly sorted company list.
The following activity diagram illustrates the workflow of the SortCommand feature:
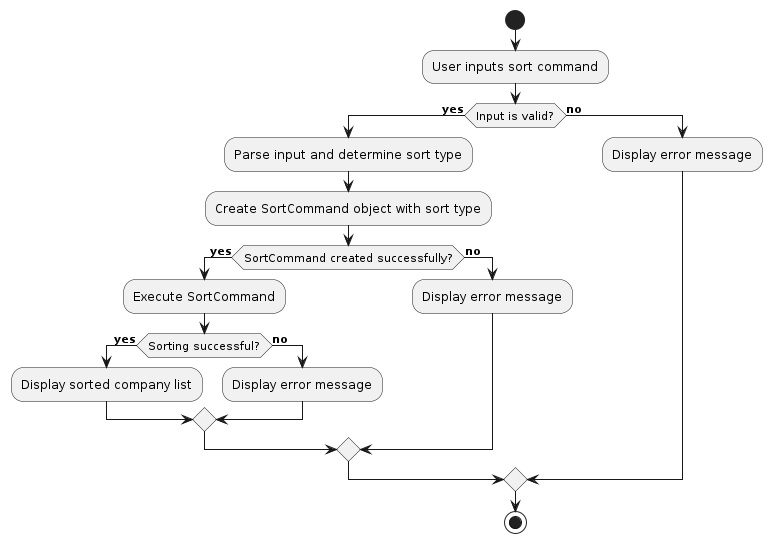
The following sequence diagram shows how sort operation is executed:
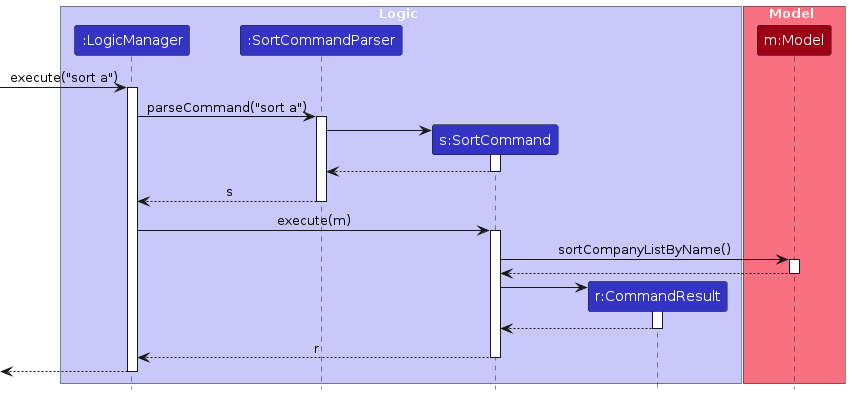
Design considerations:
Aspect: Extensibility:
Support for Future Enhancements:
Alternative 1 (current choice): Use a fixed set of sorting criteria (e.g., alphabetical order, start date order, end date order) implemented as switch cases within the SortCommand class.
- Pros: Simplified implementation, straightforward to understand and maintain.
- Cons: Limited flexibility for adding new sorting criteria in the future, may require modifications to the SortCommand class and switch cases if new sorting criteria are introduced.
Alternative 2: Implement a more flexible sorting system using a strategy pattern, where each sorting criteria is encapsulated in its own class.
- Pros: Improved extensibility, easier to add new sorting criteria without modifying existing code.
- Cons: Increased complexity in implementation, potential overhead in managing multiple sorting strategy classes.
Alternative 3: Introduce a dynamic sorting configuration where users can define custom sorting criteria through a configuration file or user interface.
- Pros: Highly customizable, allows users to define sorting criteria based on their specific needs.
- Cons: Increased complexity in implementation and management, potential challenges in ensuring user-friendly configuration interfaces.
Mark/Unmark feature
Implementation
The mark/unmark mechanism is facilitated in two parts, the first by the MarkCommandParser, and then the MarkCommand and UnmarkCommand which extends the Command abstract class.
These commands allow users to mark and unmark companies, respectively, to keep track of their application status and interest.
Both commands interact with the Model and Company classes to update the application status of a company.
The following operations are implemented to support the Mark and Unmark feature:
ModelManager#markCompany(Company company)— Updates the isMarked attribute of the specified Company object to true.ModelManager#unmarkCompany(Company company)— Updates the isMarked attribute of the specified Company object to false.ModelManager#isCompanyMarked(Company company)— Returns true if the specified Company object is marked, and false otherwise.
These operations are exposed in the Model interface and are used by the MarkCommand and UnmarkCommand classes to modify the application status of a company.
The mark() and unmark() methods in the Company class are also used to update the checkbox in the CompanyCard class to reflect the application status in the UI.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the mark/unmark mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time. The ModelManager will be initialized with the initial intern book state.
Step 2. The user executes mark 1 command to mark the 1st company in the InternBook.
Step 3. The LogicManager class will parse the user input and create a MarkCommand object with the index of the company to be marked.
Step 4. The MarkCommand class extracts the Company object at the specified index from the ModelManager.
Step 5. The MarkCommand class calls the markCompany(Company company) method of the ModelManager, passing the extracted Company object as a parameter.
Step 6. The ModelManager class updates the isMarked attribute of the specified Company object to true.
Step 7. The CompanyCard class updates the checkbox in the UI by using the method checkboxIsMarked() in the Company class to reflect the marked status of the company.
Step 8. The ModelManager class updates the filtered company list in the ModelManager to reflect the changes made to the Company object.
Step 9. The MarkCommand class returns a CommandResult object with a success message to the LogicManager.
Step 10. The LogicManager class updates the ResultDisplay in the UI with the success message.
The sequence diagram below shows how the MarkCommand executes the mark operation within the Logic component:
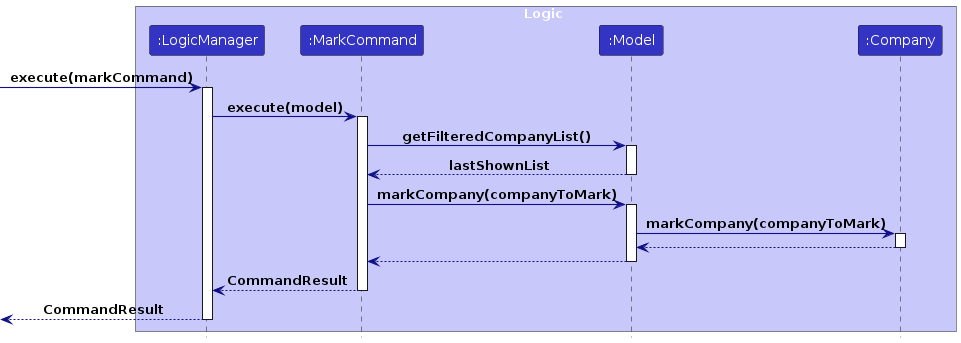
The activity diagram below summarizes the process of marking a company:
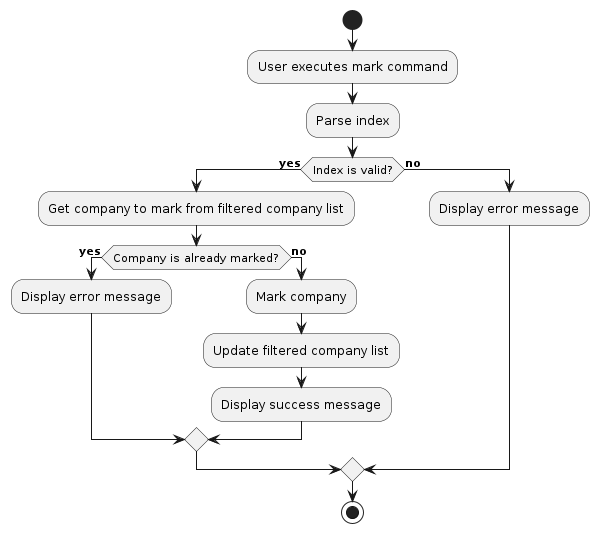
The Unmark feature follows a similar process, with the UnmarkCommand class calling the unmarkCompany(Company company) method of the ModelManager to update the isMarked attribute of the specified Company object to false.
Design considerations:
Aspect: How mark/unmark executes:
- Alternative 1 (current choice): Uses a boolean attribute in the
Companyclass to track the application status.- Pros: This approach keeps all company data within a single list, making it easier to manage and update the application status.
- Cons: May not be suitable for more complex application status tracking requirements.
- Alternative 2: Uses a separate
Markclass to track the application status.- Pros: Allows for more complex application status tracking requirements.
- Cons: May require additional classes and methods to manage the application status, making it more complex to implement and maintain.
We chose Alternative 1 because it is simpler to implement and maintain, and meets the current requirements for tracking the application status of companies.
[Proposed] Undo/redo feature
Proposed Implementation
The proposed undo/redo mechanism is facilitated by VersionedInternBook. It extends InternBook with an undo/redo history, stored internally as an internBookStateList and currentStatePointer. Additionally, it implements the following operations:
VersionedInternBook#commit()— Saves the current intern book state in its history.VersionedInternBook#undo()— Restores the previous intern book state from its history.VersionedInternBook#redo()— Restores a previously undone intern book state from its history.
These operations are exposed in the Model interface as Model#commitInternBook(), Model#undoInternBook() and Model#redoInternBook() respectively.
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the undo/redo mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time. The VersionedInternBook will be initialized with the initial intern book state, and the currentStatePointer pointing to that single intern book state.

Step 2. The user executes delete 5 command to delete the 5th company in the intern book. The delete command calls Model#commitInternBook(), causing the modified state of the intern book after the delete 5 command executes to be saved in the internBookStateList, and the currentStatePointer is shifted to the newly inserted intern book state.
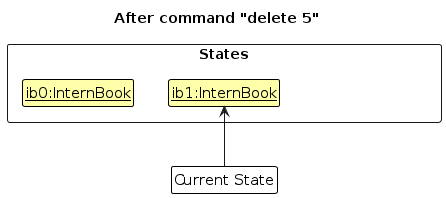
Step 3. The user executes add n/DBS … to add a new company. The add command also calls Model#commitInternBook(), causing another modified intern book state to be saved into the internBookStateList.
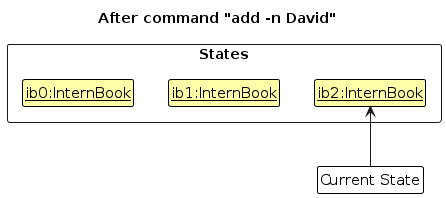
Note: If a command fails its execution, it will not call Model#commitInternBook(), so the intern book state will not be saved into the internBookStateList.
Step 4. The user now decides that adding the company was a mistake, and decides to undo that action by executing the undo command. The undo command will call Model#undoInternBook(), which will shift the currentStatePointer once to the left, pointing it to the previous intern book state, and restores the intern book to that state.
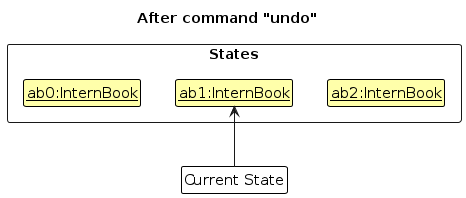
Note: If the currentStatePointer is at index 0, pointing to the initial InternBook state, then there are no previous InternBook states to restore. The undo command uses Model#canUndoInternBook() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather
than attempting to perform the undo.
The following sequence diagram shows how an undo operation goes through the Logic component:
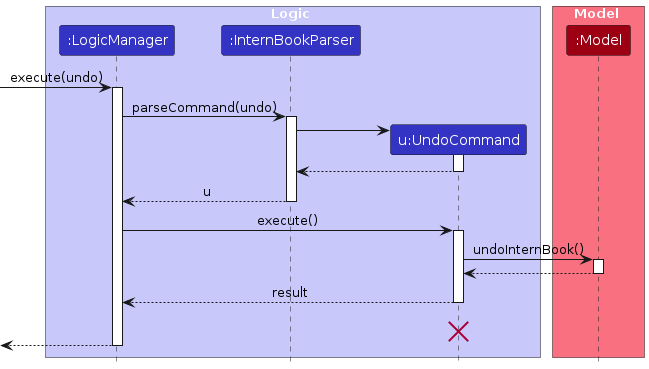
Note: The lifeline for UndoCommand should end at the destroy marker (X) but due to a limitation of PlantUML, the lifeline reaches the end of diagram.
Similarly, how an undo operation goes through the Model component is shown below:
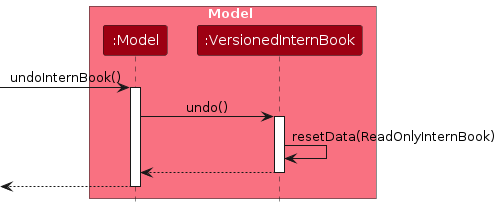
The redo command does the opposite — it calls Model#redoInternBook(), which shifts the currentStatePointer once to the right, pointing to the previously undone state, and restores the intern book to that state.
Note: If the currentStatePointer is at index internBookStateList.size() - 1, pointing to the latest intern book state, then there are no undone InternBook states to restore. The redo command uses Model#canRedoInternBook() to check if this is the case. If so, it will return an error to the user rather than attempting to perform the redo.
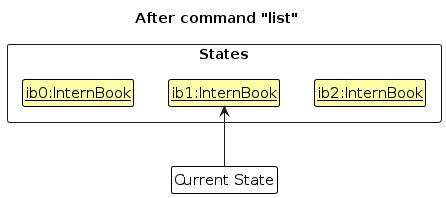
Step 5. The user then decides to execute the command list. Commands that do not modify the intern book, such as list, will usually not call Model#commitInternBook(), Model#undoInternBook() or Model#redoInternBook(). Thus, the internBookStateList remains unchanged.
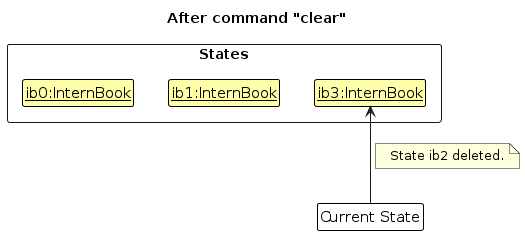
Step 6. The user executes clear, which calls Model#commitInternBook(). Since the currentStatePointer is not pointing at the end of the internBookStateList, all intern book states after the currentStatePointer will be purged. Reason: It no longer makes sense to redo the add n/DBS … command. This is the behavior that most modern desktop applications follow.
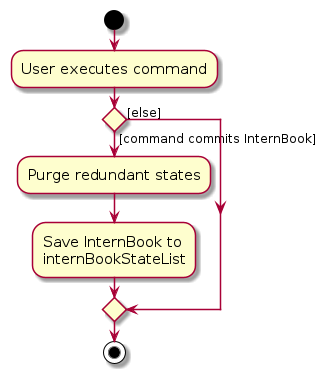
The following activity diagram summarizes what happens when a user executes a new command:
Design considerations:
Aspect: How undo & redo executes:
Alternative 1 (current choice): Saves the entire intern book.
- Pros: Easy to implement.
- Cons: May have performance issues in terms of memory usage.
Alternative 2: Individual command knows how to undo/redo by itself.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
delete, just save the company being deleted). - Cons: We must ensure that the implementation of each individual command are correct.
- Pros: Will use less memory (e.g. for
[Proposed] Data archiving
Proposed Implementation
The proposed data archiving mechanism is facilitated by ArchiveAddressBookStorage. It implements AddressBookStorage with an option to store as JSON or CSV
ArchiveAddressBookStorage#StoreJSON()— Saves the current intern book inJSONformat.ArchiveAddressBookStorage#StoreCSV()— Saves the current intern book inCSVformat.
These operations are exposed in the Storage interface as Storage#StoreJSON() and Storage#StoreCSV().
Given below is an example usage scenario and how the data archiving mechanism behaves at each step.
Step 1. The user launches the application for the first time. The ArchiveAddressBookStorage will be initialized with the initial intern book state.
Step 2. The user executes Archive JSON command to archive the active InternBook by calling the Storage#StoreJSON() method.
Documentation, testing, logging, configuration, dev-ops
Appendix: Requirements
Product scope
Target user profile:
- has a need to keep track of significant internship applications made
- prefer desktop apps over other types
- can type fast
- prefers typing to mouse interactions
- is reasonably comfortable using CLI apps
Value proposition: easily keep track and view internship applications better than typical mouse/GUI driven app
User stories
Priorities: High (must have) - * * *, Medium (nice to have) - * *, Low (unlikely to have) - *
| Priority | As a … | I want to … | So that I can… |
|---|---|---|---|
* * * | user | add details of company | easily keep track of companies I am interested in |
* * * | user | list companies added | view all the companies that I am currently interested in |
* * * | user | delete a company | remove company that I am no longer interested in |
* * * | user | save my data | view my list from previous sessions without re-entering my list |
* * | user | find a company by name | locate details of company without having to go through the entire list |
* * | user who is interested in many companies | sort companies | view the list in my preferred order |
* * | user | set application dates | easily keep track of the company's applications openings and deadlines |
* * | user | get reminders | ensure that I will not miss out on any applications |
* * | user | mark a company as applied | easily identify companies that I have applied for |
* * | user | unmark a company as applied | easily undo a mistake when I marked a company as applied |
* | user | archive companies that I have already applied to | keep my company list organized and refer to it when I need to |
{More to be added}
Use cases
(For all use cases below, the System is the InternBook and the Actor is the user, unless specified otherwise)
Use case: Add a company (UC-01)
MSS
User requests to add a company.
InternBook shows User the company it is going to add.
InternBook adds company.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given input is invalid.
1a1. InternBook shows an error message.
Use case ends.
1b. The company already exists in the current InternBook.
1b1. InternBook shows an error message.
Use case ends.
Use case: Delete a company (UC-02)
MSS
User requests to list companies.
InternBook shows User a list of companies.
User requests to delete a specific company in the list.
InternBook shows User the company it is going to delete.
InternBook deletes the company.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
3a. The given index is invalid.
3a1. InternBook shows an error message.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: List all companies (UC-03)
MSS
User requests to list companies.
InternBook shows User a list of companies.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
Use case: Sort all companies (UC-04)
MSS
User requests to list companies.
InternBook shows User a list of companies.
User requests to sort the list in specified order.
InternBook shows User a sorted list of companies.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
3a. The given preference is invalid.
3a1. InternBook shows an error message.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: Find a company (UC-05)
MSS
User requests to list companies.
InternBook shows User a list of companies.
User requests to find companies and tags that satisfies a keyword.
InternBook shows User the companies and tags satisfying the keyword.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
3a. There are no companies satisfying the keyword.
3a1. InternBook shows user an empty list.
Use case ends.
Use case: Mark a company (UC-06)
MSS
User requests to list companies.
InternBook shows User a list of companies.
User requests to mark a specific company in the list.
InternBook marks the company.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
3a. The given index is invalid.
3a1. InternBook shows an error message.
Use case resumes from step 2.
3b. The company at the given index is already marked.
3b1. InternBook shows an error message.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: Unmark a company (UC-07)
MSS
User requests to list companies.
InternBook shows User a list of companies.
User requests to unmark a specific company in the list.
InternBook unmarks the company.
Use case ends.
Extensions
2a. The list is empty.
Use case ends.
3a. The given index is invalid.
3a1. InternBook shows an error message.
Use case resumes from step 2.
3b. The company at the given index is already unmarked.
3b1. InternBook shows an error message.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: Setting reminders (UC-08)
Brief Description: This use case outlines the steps for a user to set reminders within InternBook application and manage their preferences regarding reminders.
Preconditions:
- The user has launched InternBook.
MSS
User requests to set a reminder.
InternBook saves the reminder based on the user's input.
User exits InternBook.
At a later time, the user launches InternBook again.
InternBook displays a separate window showing applications that needs reminder.
User requests to switch off reminders.
InternBook updates the user's preference to turn off reminders
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given input is invalid.
1a1. InternBook shows an error message.
Use case resumes from step 2.
Use case: Edit a company (UC-09)
MSS
User requests to edit a company.
InternBook shows User the company it is going to edit.
InternBook edits company.
Use case ends.
Extensions
1a. The given input is invalid.
1a1. InternBook shows an error message.
Use case ends.
{More to be added}
Non-Functional Requirements
- Should work on any mainstream OS as long as it has Java 11 (it might not work on older or newer versions).
- Should be able to hold up to 1000 companies without a noticeable sluggishness in performance for typical usage.
- A user with above average typing speed for regular English text (i.e. not code, not system admin commands) should be able to accomplish most of the tasks faster using commands than using the mouse.
- The code should be well-documented and structured in a way that makes it easy to maintain and upgrade.
- Should be able to store data locally on the user's machine using properly formatted text files or CSV.
- Should ensure the integrity of the data in the local storage files, with appropriate error handling to prevent data corruption.
- A user should be able to export and import their data easily.
- Should guide users towards the correct action with clear and informative error messages when the user enters an invalid input.
Glossary
- Mainstream OS: Windows, Linux, Unix, MacOS
- Previous Session: The session that the user previously used the application, and exited the application successfully without any errors.
- Local Storage: The storage of data on the local filesystem of the user's computer, as opposed to an online or networked database.
- CSV (Comma-Separated Values): A file format used for storing tabular data, where each line of the file is a data record, and each record consists of one or more fields separated by commas.
- Text File: A standard text file, often with a .txt extension, that contains unformatted generic text content.
Appendix: Instructions for manual testing
Given below are instructions to test the app manually.
Note: These instructions only provide a starting point for testers to work on; testers are expected to do more exploratory testing.
Launch and shutdown
Initial launch
Download the jar file and copy into an empty folder
Double-click the jar file Expected: Shows the GUI with a set of sample contacts. The window size may not be optimum.
Saving window preferences
Resize the window to an optimum size. Move the window to a different location. Close the window.
Re-launch the app by double-clicking the jar file. Expected: The most recent window size and location is retained.
Adding a company
Adding a company
Prerequisites: None
Test case:
add -n ABC -e abc@abc.com -t XYZExpected: Contact with nameABC, emailabc@abc.com, tagXYZis added to the bottom of the list. Details of the added contact shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is reset.Test case:
add -e abc@abc.com -t XYZExpected: No company is added. Error details shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is not reset.Other incorrect add commands to try:
add,add -n ABC -t XYZ,...Expected: Similar to previous.
Deleting a company
Deleting a company while all companies are being shown
Prerequisites: List all companies using the
listcommand. Multiple companies in the list.Test case:
delete 1Expected: First contact is deleted from the list. Details of the deleted contact shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is reset.Test case:
delete 0Expected: No company is deleted. Error details shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is not reset.Other incorrect delete commands to try:
delete,delete x,...(where x is larger than the list size) Expected: Similar to previous.
Editing a company
Editing a company
Prerequisites: List all companies using the
listcommand. Multiple companies in the list.Test case:
edit 1 -n ABCExpected: Edits the contact at index 1 to change its name toABC. Details of the edited contact shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is reset.Test case:
edit 0 -e abc@abc.com -t XYZExpected: No company is edited. Error details shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is not reset.Other incorrect edit commands to try:
edit,edit x -n ABC,edit -n ABC -t XYZ,...(x is an index our of range) Expected: Similar to previous.
Locating a company
Locating a company
Prerequisites: List all companies using the
listcommand. Multiple companies in the list.Test case:
find ABCExpected: Finds all contacts with either name or tag beginning withABC. The number of companies found is shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is reset.Test case:
findExpected: No company is found. Error details shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is not reset.
Marking a company
Marking a company
Prerequisites: List all companies using the
listcommand. Multiple companies in the list. Company you want to mark has not already been marked.Test case:
mark 1Expected: Marks the contact at index 1 to tick the box on its right. Details of the marked contact shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is reset.Test case:
mark 0Expected: No company is marked. Error details shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is not reset.Other incorrect mark commands to try:
mark,mark x,mark t,...(x is an index our of range, t is an index which is already marked) Expected: Similar to previous.
Unmarking a company
Unmarking a company
Prerequisites: List all companies using the
listcommand. Multiple companies in the list. Company you want to unmark has not already been unmarked.Test case:
unmark 1Expected: Unmarks the contact at index 1 to remove the tick on the box on its right. Details of the unmarked contact shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is reset.Test case:
unmark 0Expected: No company is unmarked. Error details shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is not reset.Other incorrect unmark commands to try:
unmark,unmark x,unmark t,...(x is an index our of range, t is an index which is already unmarked) Expected: Similar to previous.
Sorting companies
Sorting companies
Prerequisites: List all companies using the
listcommand. Multiple companies in the list.Test case:
sort aExpected: Sorts the contacts in alphanumerical order. Successful sorting message is shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is reset.Test case:
sort gExpected: No company is sorted. Error details shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is not reset.Other incorrect sort commands to try:
sort,sort a bc,sort 1,...Expected: Similar to previous.
Setting reminder
- Setting number of days for reminder window to show applications that is number of days till the end date.
- Test case:
reminder -r -1Expected: Error message should be shown as the number of days should be positive. - Test case:
reminder -r 10Expected: Number of days is set to 10 so the reminder window should contain applications with end date 10 days away. - Test case:
reminder -r offExpected: The reminder feature is switched off.
- Test case:
Clearing the InternBook
Clearing the InternBook
Prerequisites: List all companies using the
listcommand. Multiple companies in the list.Test case:
clearExpected: Clears all the contacts in the InternBook. Successful clear message shown in the status message. Text in the status bar is reset.
Exiting the InternBook
Exiting the InternBook
Prerequisites: None
Test case:
exitExpected: Closes the InternBook and exits it.
Saving data
Dealing with missing/corrupted data files
- Test case: Manually edit the
addressbook.jsonfile to have invalid data. Expected: The InternBook starts as an empty InternBook
- Test case: Manually edit the